The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and trends in the smart factory are redefining today’s OEM business model. Overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) and zero equipment downtime are no longer just buzzwords because they are now key measures of a successful business. In order to provide these services, machine builders need an effective way to gain visibility into their machines and be able to remotely connect to and manage their machines at field sites. In this article, we discuss five key elements of a secure remote access solution for industrial equipment and explain why a cloud-based remote access solution is ideal for machine builders.
Traditional remote access solutions, such as a virtual private network (VPN) and remote desktop connection (RDC), have been providing secure remote access to networks and systems in organizations. However, many of these solutions lack the flexibility or the intelligence to meet the specific needs of industrial machine builders. The five key elements that such machine builders have to consider when they use VPN and RDC solutions are:
1. Time-Consuming Setup Process that Requires Extensive IT Knowledge
Multiple parameters need to be configured to build connectivity with remote machines and to be able to exchange the necessary authentication keys and data. The process of setting up VPN and RDC connections is complex, time consuming, and requires extensive IT knowledge.
2. Compromises in Corporate Security Policies Required to Enable Remote Access to Machines
VPN applications require a VPN server to have a static public IP address, and some specific network ports need to be configured to permit inbound and outbound traffic. Most IT departments are unwilling to implement these changes in their organization’s network because the changes may create network vulnerabilities and compromise network security.
3. The Complexity and the High Cost of Ensuring Security of Remote Connections
VPN connections between machine builders and machine operators are usually site-to-site connections, which typically provide a machine builder remote access to all local devices in a plant's network. The only way to mitigate this security risk is for IT departments to create separate end-to-end connections using VPN technology, which is complex and expensive, and drastically increases maintenance costs.
RDC connections are equally troublesome in that they expose computing equipment on the plant network to the public network, creating security risks. Mitigating these security issues requires additional resources, both in terms of human resources and setup and maintenance costs.
4. VPN Security Is Hard to Manage
One way to achieve a higher level of security is to have different pre-shared keys or X.509 certificates for each VPN tunnel. When the number of VPN connections required is few, it is easy to manage the keys or certificates for these connections. However, as the number of VPN tunnels grows, it would be very hard to manage these keys and certificates.
5. Scalability and Flexibility Come at a High Cost
VPN servers typically have a limitation on the number of VPN tunnels they can support. When a business grows, more and more machines and devices are connected, with an increasing number of engineers supporting business operations. The proliferation of machines and devices leads to an increase in the number of VPN connections required. Once this number exceeds the VPN server’s capabilities, machine builders will need to install a new VPN server and go through the time-consuming configuration process all over again.
Because of these limitations and restrictions in VPN and RDC-based remote access solutions, machine builders and equipment manufacturers are looking for easy-to-use, secure, flexible, and scalable solutions that can be used to remotely manage their machines and equipment.
Cloud-Based Secure Remote Access
Cloud-based remote access is a new type of remote access solution that enables flexible remote access to field machines. The network topology of a cloud-based remote access solution has three components: a remote gateway, a cloud server, and client software. Remote gateways are connected to field equipment in order to remotely access and control them. Client software is installed on the engineer’s PC. The cloud server can be installed on a cloud-based platform such as Amazon Web Service or Microsoft Azure. The remote gateway and client software will both initiate outbound secure connection requests to the cloud server. The cloud server will map the two connection requests and after successful authentication on both sides, a connection will be established.
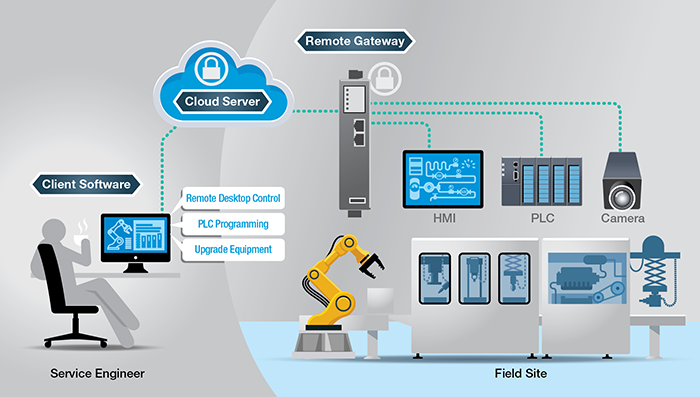
Moxa has designed the Moxa Remote Connect (MRC) solution specifically for OEMs and machine builders to help them improve their efficiency and lower operational cost. For additional details, visit Moxa Remote Connect and download our link to this white paper.