When it comes to enhancing industrial network security the first question that often arises is “How to start?” Ramping up the network security of industrial applications is akin to bolstering the security of your home. You can lock the doors and windows, set up an IP surveillance system, and store your valuables in a safe. The more actions you take, the more secure your home is. Similar to securing an industrial network, the more security you want, the more procedures you have to implement. The decision of how much security you want often depends on the level of risk you can accept, the level of security you hope to achieve, as well as your ability to implement the security.
As different companies have different levels of maturity regarding the implementation of cybersecurity (ARC, 2019 ), it is challenging to recommend a singular approach that fits all of them. We intend to present the IEC 62443 set of standards as suitable cybersecurity guidelines for any critical industrial process. We will primarily focus on the technologies that are used with network infrastructure assets and present a systematic and automatic approach to configuration that helps avoid human error. This approach helps verify the existing functionalities of each device connected to a network, by ensuring they match the guidelines suggested by the IEC 62443 standard and to alert users if device configurations do not meet the minimum requirements.
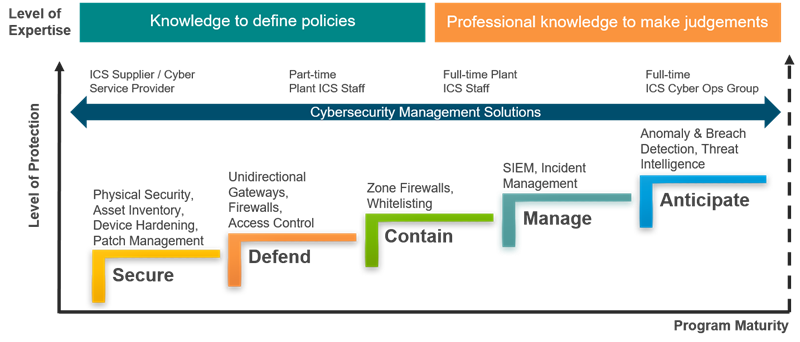
Figure 1: The Cybersecurity Maturity Model suggested by the ARC Advisory Group.
A Systematic Approach
The use of a systematic and predominately automatic approach to implementing configurations is essential to ensure uniformity and, more importantly, a consistent and reliable repeatability of the configurations. This approach aims to reduce the amount of tasks that humans have to perform manually during the process, as the human factor is considered a major cause of cyberincidents, regardless of whether they were intentional or not. Further compounding this problem is the fact that vulnerabilities caused by human error are difficult to detect. This is because the detection often relies on the audit process that a company has implemented, which may not be 100% reliable. Last, those who perform the configurations may falsely believe that they have made the proper implementations, which in turn leaves the networks vulnerable.
It is important to give attention to not only the methodologies themselves, i.e., 'What to implement', but also to the way in which they are implemented, 'The how'. By taking a systematic and automatic approach to implement the configurations, these risks can be considerably reduced, increasing the reliability and security of the networks.
Software-aided Implementation
Software can be one of the “how” options that allows you to successfully implement security procedures. Even the most experienced engineer cannot memorize all the configurations needed for these security procedures. Another issue that further compounds the problem is when companies want to manage the configurations and keep them consistent throughout the network life cycle. Below are three tips when using software to perform configurations.
Developing Checklists for Implementing Security Measures
Before your engineers start performing configurations, it is essential to provide them with clear guidelines by compiling a checklist based on your companies’ security policies. According to the IEC 62443 standard, you need to consider five stages (Figure 2). For instance, it is highly recommended to enable username and password protection to verify user identification when logging into devices, despite the temptation to not have security measures as it is much easier and quicker to access devices without password protection.

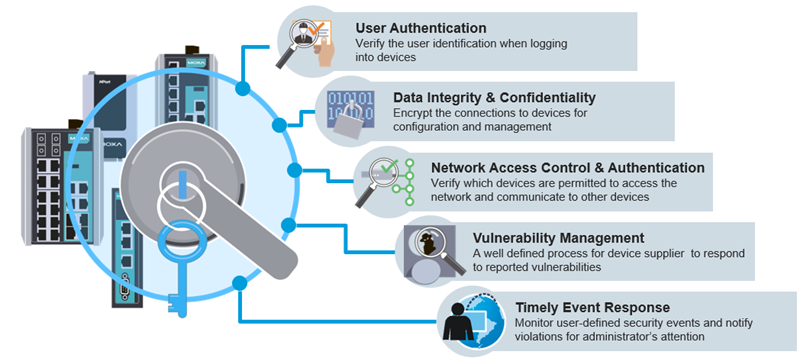
Figure 2: Five stages to examine the security measures.
Using Images Rather Than Lists
One of the most efficient ways to support the security checking process without compromising user judgment is to use graphical representations rather than lists to identify equipment on networks. Images are processed faster and are easier to recognize by the human brain. Therefore, using graphical representations helps quicken the identification of the security settings of each device, as shown in Figure 3.
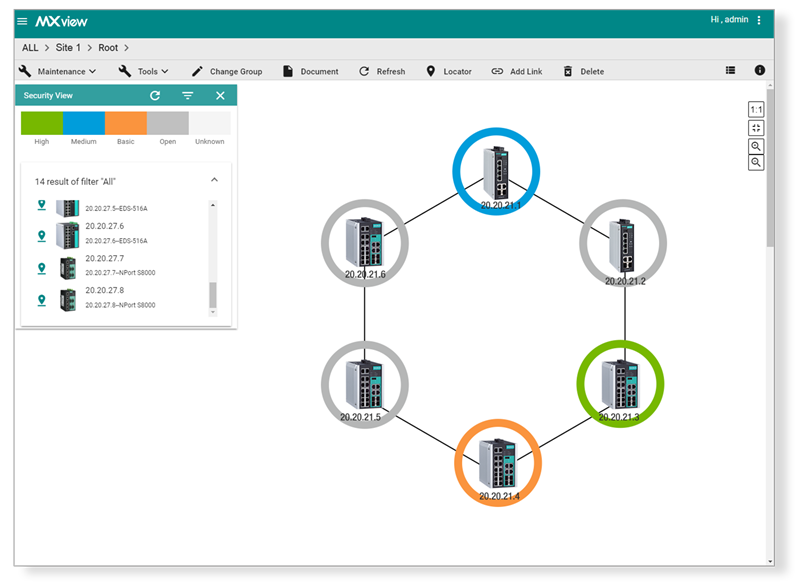
Figure 3: Graphical architecture with color system security status.
Using Colors
The final point that we will consider is color differentiation to highlight different levels of security. The human brain can easily recognize different color tones (Engel S, Zhang X, Wandell B, 1997), which means that different colors can be used to offer the user a quick identification of the security status of each device and inform them of possible actions that have to be taken.
Summary
In conclusion, systematic and automatic methods are more reliable than repetitive and manual processes performed by humans. It is essential that all existing cybersecurity features are suitable for the individual needs of each system and are implemented correctly. Taking a systematic approach may assist you to deal with complex security configurations, while at the same time reducing human error.
Moxa’s MXview network management software provides you with a holistic view of the security status of your networking devices and MXconfig configuration software allows you to mass configure the security parameters to ramp up your network security. Furthermore, Moxa has also produced security checklists for its Ethernet switches and serial device servers to help users implement security measures. Visit the microsite to learn more.