NPorts are serial-to-Ethernet devices and hence they communicate with the Real COM driver over a TCP/IP network. This results in slower read/write performance on the Real COM port when compared to native COM ports, especially when the network traffic is heavy.
To improve the performance of the Real COM port on your NPort device, you can try modifying the following advanced settings:
- Fast Flush
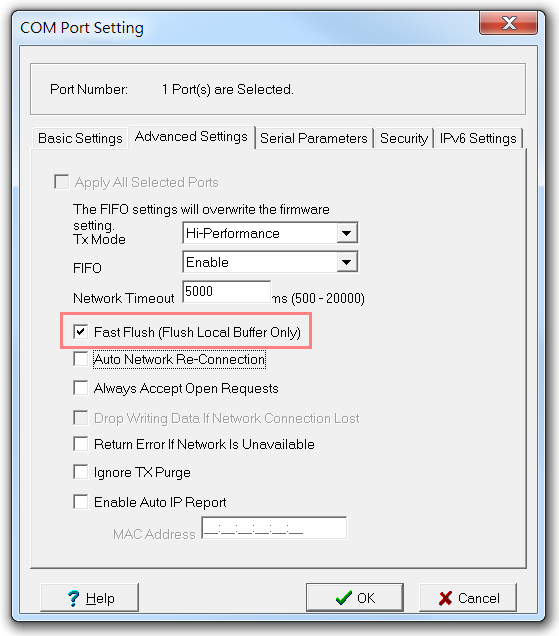
If your program is using the Win32 PurgeComm function, this might be the reason for your NPort’s poor performance. You can try to improve the performance of your NPort by enabling the Fast Flush function.
For example, in an NPort 6000, open the Windows Driver Manager, go to the Advanced Settings page, and select the Fast Flush (Flush Local Buffer Only) option.
- Tx Mode
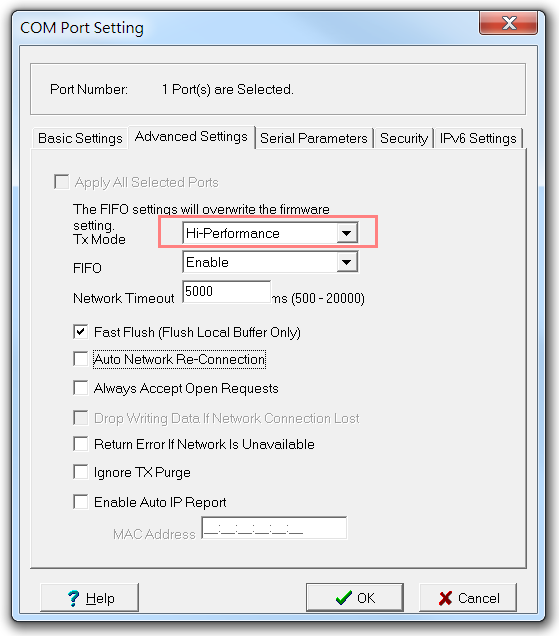
There are two options available for the Tx Mode field–Hi-Performance and Classical Mode. The Classical mode option may be the cause of your NPort’s poor performance. You can switch to the Hi-Performance mode for higher data throughput.
For example, in an NPort 6000, open the Windows Driver Manager, go to the Advanced Settings page, and select the Hi-performance option for Tx Mode.
- FIFO
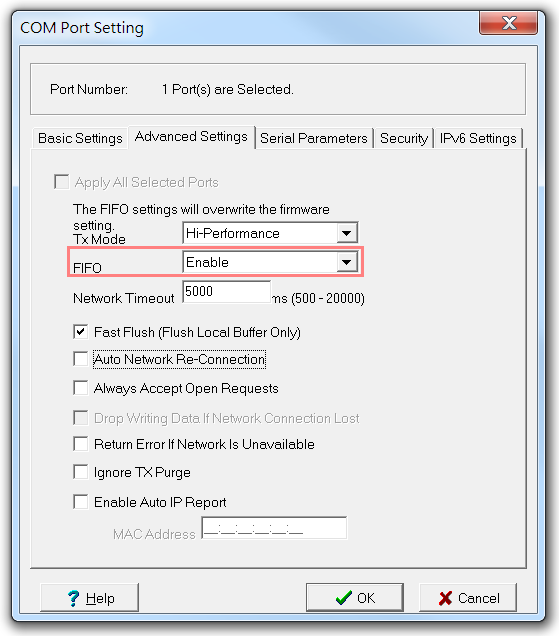
If your data is transmitted in small packets from serial to Ethernet, the NPort will take a long time to handle the data, leading to poor performance. You can try to improve the performance by enabling FIFO (First-In-First-Out).
For example, in an NPort 6000, open the Windows Driver Manager, go to the Advanced Settings page, and select the Enable option for FIFO.
For additional details, refer to your NPort’s User Manual.
If the above mentioned settings do not help improve the performance of the Real COM port on your NPort, use the PortMon* tool to capture the device log and send it to Moxa’s Support Team.
*PortMon is a free utility that monitors and displays all serial port activity on a system.